What is Biomass
Biomass is an organic material which can be turned into electricity, fuel, and heat. Biomass is typically derived from sustainable forestry, forestry residues, and other sustainable ‘crops’ like willow.
Biomass is any organic material made from Agricultural& Wood plants and Animal & Municipal Waste etc.

Examples of biomass material are:
-
Agricultural Residue
- Switchgrass
- Cotton Gin Waste (briquette made of cotton gin waste-2nd picture down)
- Grape, Olive & Fruit Pomace
- Oat Hulls
- Coffee Bean Hulls
- Miscanthus
- Nut Shells, Skins and Hulls
- Corn Husk & Cobs
- Wheat Mids
- Bagasse (4th picture down)
-
Wood Waste
- Construction & Demolition Material
- Medium Density Fiber Board (MDF)
- Sawdust and Sanding Dust
- Bark, Shavings, Cut-Offs (3rd picture down)
- Pulp & Paper Waste
- Pallets & Mulch
-
Animal & Municipal Waste
- Bedding
- Manure
- Litter
- Dairy Washdown
- Organic Municipal Solids
- Industrial/Commercial Waste
- Wood Crates & Pallets
- Paper/Cardboard
- Pulp
The applications for solid biomass fuels are numerous and the supply of biomass materials is seemingly endless.
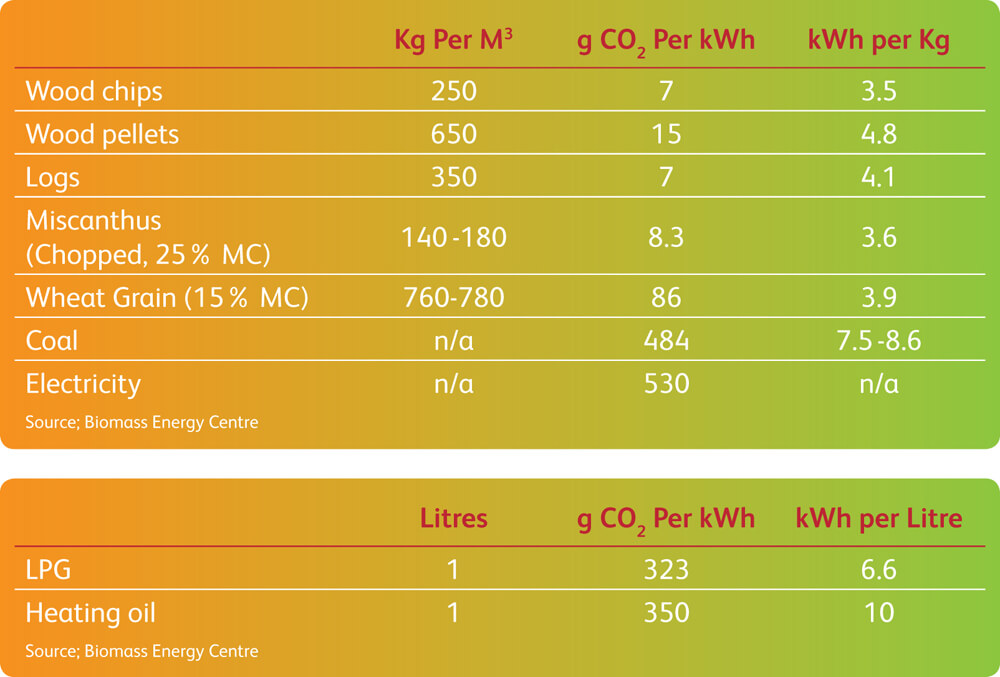
The table below gives an overview of the relative densities per cubic metre, the CO2emitted per kWh of heat generated and how many units of heat in kWh may be gained from different biomass fuels.